How to share a link to an article
Sharing links to articles within Concordia
To successfully share a link, the address must be “permanent”, “stable” or “persistent”. Unlike most other links, permanent links remain active and useable over time. For free e-resources, only the publisher’s permanent link needs to be used.
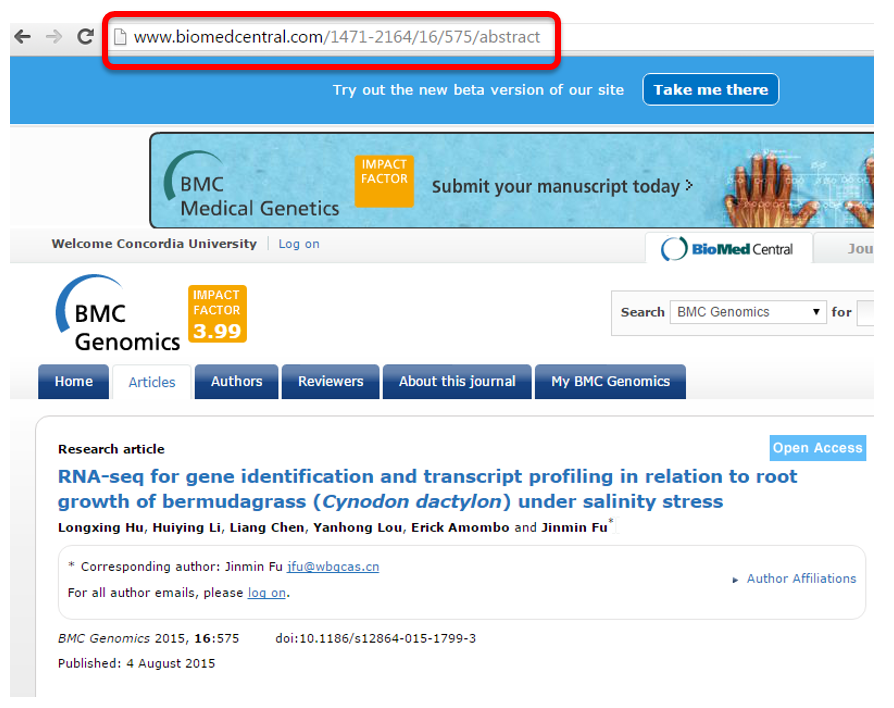
When Concordia Library subscribes to electronic resources, publishers recognize the web address of Concordia University as one that can have legitimate access to these resources. While in the library or anywhere else on campus, access to Library subscribed resources is seamless. Off-campus access, however, requires adding the Concordia web address to the address of the resource. This serves as a “proxy” to allow you access to Concordia e-resources and will prompt authentication with your Concordia netname.

Finding a permanent link
When you have found an article through a search of Concordia Library's databases, this means that Concordia Library has a subscription to it. Most database providers, such as EBSCO and ProQuest, offer permalinks:
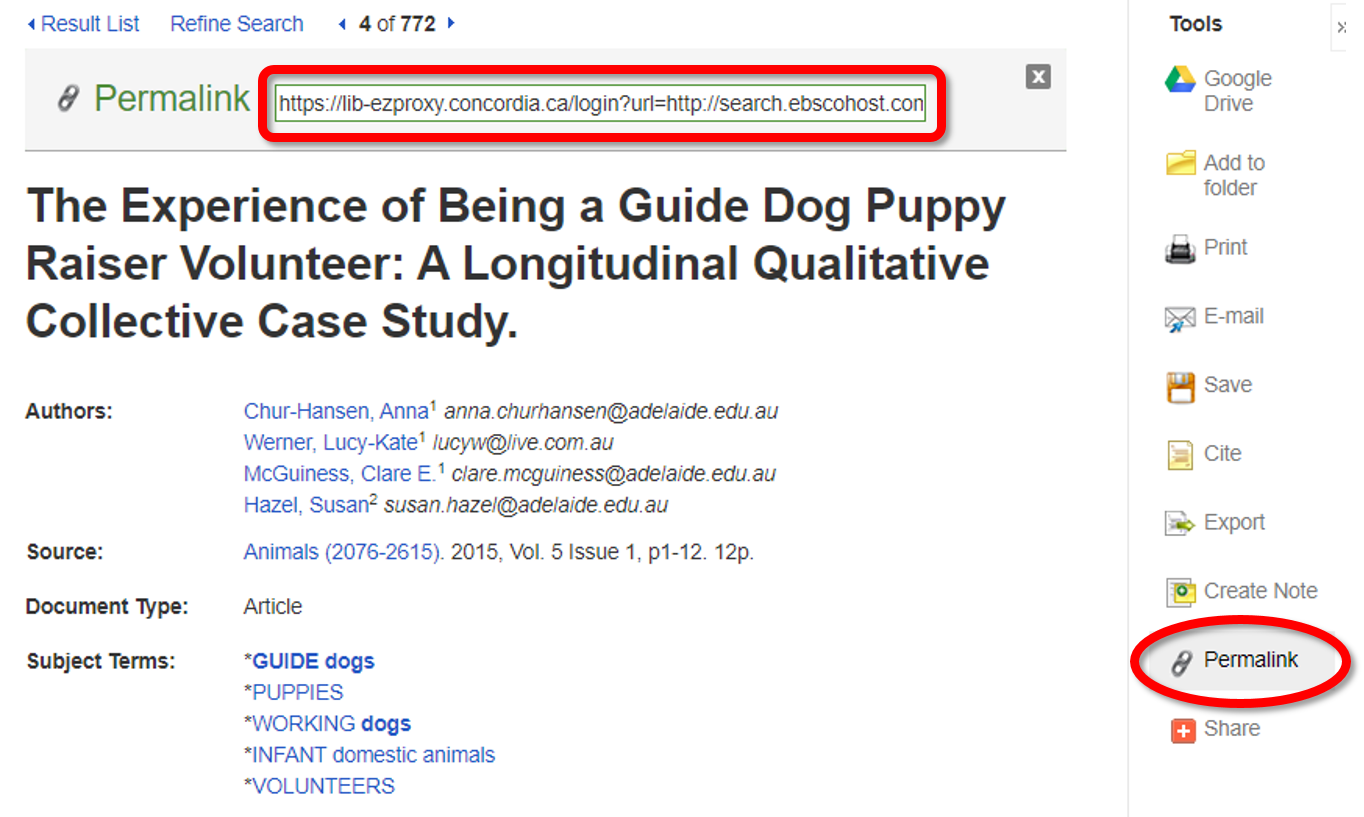
If the database offers both a permanent link and a DOI, the permanent link is preferable when sharing links with your students or colleagues from Concordia:
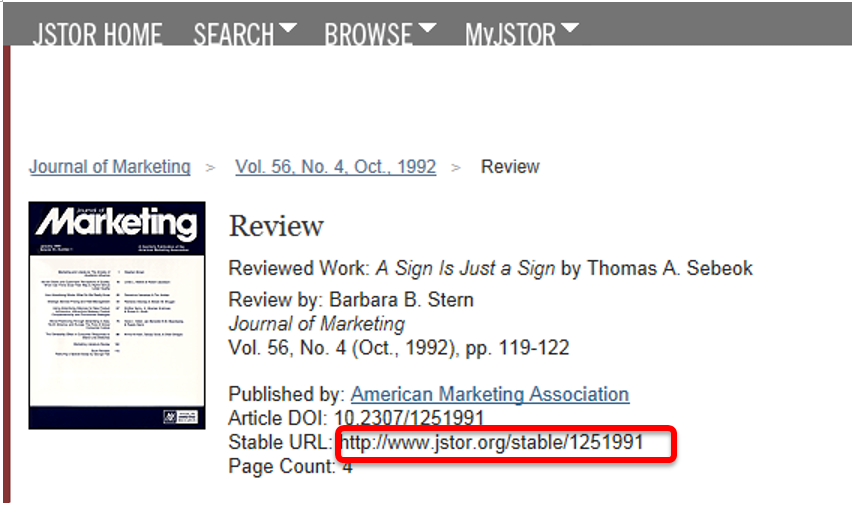
Please note that the stable URL in the above example requires a proxy (see Creating a permanent link).

Creating a permanent link
For resources that require paid subscriptions, you will need to add the Library's proxy in order to make a permanent link accessible outside of the University campus.
For example, to convert the following link to a permanent link,
https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=87680413&site=ehost-live
The proxy address must be incorporated:
https://lib-ezproxy.concordia.ca/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=87680413&site=ehost-live&scope=site

DOI permanent links
Sometimes you will see only a DOI, and not a permanent link, when viewing the citation information for an article. A DOI is a standardized method for identifying an electronic object. DOIs often appear in the citation or the abstract of an article or even in its full-text format.
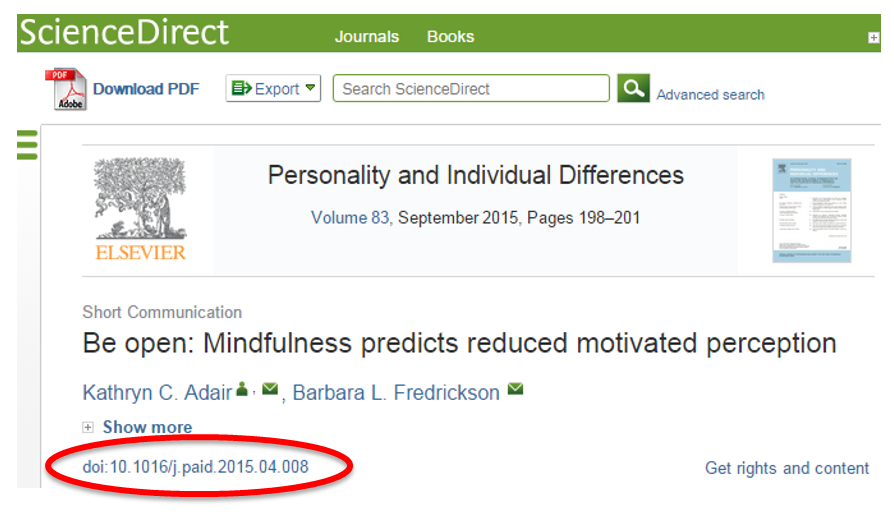
When you have located a DOI, follow these steps to complete the link.
To convert the DOI to a URL, precede it with the following:
https://dx.doi.org/
For example, the doi:10.1016/j.paid.2015.04.008 becomes:
https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.04.008
This is sufficient if the article is available for free.
To create a link to an article that Concordia Library subscribes to, the Library's proxy must also be added to your URL. For example:
https://lib-ezproxy.concordia.ca/login?url=https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.04.008
Tip: If you cannot find the DOI of an article, try using the following tool: https://www.crossref.org/guestquery/


