Searching
Basic search
By default, the library website is set to basic search, where a single query box appears.
With this type of generic search, you may find items with keywords (subject, author, title, date of publication, editor, ISBN), using a single word or phrase with several words.
Basic search examples:
- margaret atwood
- nanotechnology
- indigenous art
- capital in the twenty-first century
To narrow search results or to initiate a more complex search, choose the advanced search functionality, or use search filters with indexes. To find a specific publication, enter the title and author in the advanced search box.

Advanced search
This functionality is a more complete form to specify various criteria, which appears by clicking on "Advanced Search" in the navigation bar, under the Sofia logo.

Advanced search includes different types of boxes, where users specify their criteria, or "index". This includes different types of information to describe an item (title, author, editor, year of publication, language, ISBN, etc.).
You may add search boxes with the "+" button.
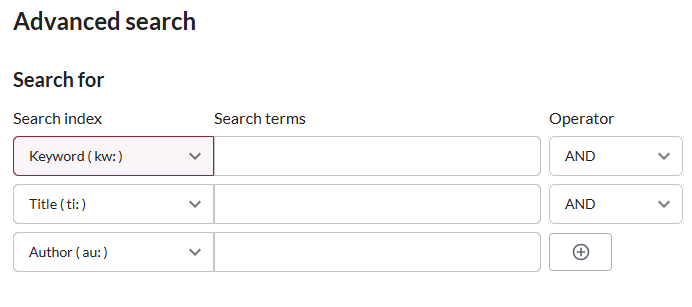
Advanced search includes other options:
- Search a specific database or group of databases;
- Narrow results to open access or scientific articles;
- Request a specific format;
- Specify a range of publication dates;
- Select a branch or library
Search tips
To avoid incomplete search results, follow these guidelines for keywords:
| Case | The case does not affect search results. Keywords are upper case, lower case, or a combination of both. However, Boolean operators must be in upper case. |
| Stop words | Avoid French or English stop words (le, la, les, du, de, des, a, an, but, the, etc.) because the Sofia Discovery tool does not take them into account. Use quotation marks (" ") for stop words that must be taken into account with the search.
Example: Thé = "the". |
| Punctuation and diacritics | Avoid punctuation or diacritical signs.
Example: é=e, à=a, ç=c, ù=u, etc. |
| Apostrophe (') | Avoid apostrophes (') and the letter preceding them, or omit the apostrophe and space between the words preceding and following the apostrophe. To include all variations, link both options with a Boolean OR.
Example: for king's, enter king OR kings |
| Numbers | Numbers may be entered in numerals or letters. |
| Hyphens | Use hyphens (-) or replace hyphens with a space.
Example: twenty-one, twenty one |

Search tips
With Sofia, you can use different types of operators to define, as accurately possible, your search criteria and language. These operators apply to basic searches and advanced searches.
Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT)
Boolean operators are inserted between keywords in a search box or between search boxes to connect or exclude certain words or phrases. For Sofia to recognize them, Boolean operators must be UPPERCASE. Keywords and their Boolean operators are processed left to right.
| AND | Narrows search results by returning only items that include both words/ phrases connected through the operator.
Example: photography AND war * If no other operator is entered in the search box, a Boolean AND is by default inserted between the words. |
| OR | Broadens search results by returning items that include either word/phrase connected through the operator.
Example: teen OR adolescent. |
| NOT | Reduces search results by excluding items that include the word/phrase after the operator.
Example: "renewable energy" NOT hydroelectricity |
More information on Boolean operators.
Quotation marks
Use English (" ") quotation marks to find an exact phrase or the closest words.
Examples:
- "attention deficit disorder"
- "Philippe Aubert de Gaspé"
Truncation
An asterisk (*) isolates the root of a word to include all variations or words from the same family. This generally increases search results. At least three letters must precede the asterisk.
Example:
- environment* = environment / environments / environmental / environmentally / environmentalism / environmentalist
More information on truncation
Wildcards
A pound sign (#) or question mark (?) substitutes one or several variable letters in a word. Wildcards broaden search results. At least three characters must precede the wildcard.
The pound sign (#) substitutes only one letter.
Examples:
- Thes#s = thesis, theses
- Wom#n = woman, women
The question mark substitutes several letters (0 - 9).
Example:
- Encyclop?dia = encyclopedia, encyclopaedia
Parentheses
Specify the order in which Boolean operators are applied to group keywords. Once the search is launched, Sofia interprets the words and operators in parentheses first, and interprets the words and operators outside the parentheses last.
Example:
- (computer* OR electronic*) AND (waste OR disposal) AND environment*
Indexes
Most search indexes are displayed in the advanced search window, but you can also enter their abbreviations in the in search boxes (basic or advanced search), and combine them with different operators.
*NOTE: a colon (:) after an abbreviation launches a keyword search in the index, but the equal sign (=) is used to find a specific phrase in the index In the latter case, the phrase must be located at the beginning of the field in question, without any words after, which significantly narrows results. When in doubt, use a colon with quotation marks.
Example:
- ti=early childhood
- means that we’re looking for documents precisely entitled “Early Childhood”. A document entitled "Early Childhood : A Survey of Best Practices" would therefore not be included in the search results.
- ti:"early childhood"
- searches for the phrase "early childhood" wherever it may be within the title field, even in combination with other words.
The following list includes the most commonly used indexes and their abbreviations:
| Author | au:shakespeare
au=shakespeare william |
| Call number | nu:PS 3515*
nu=QD 96 M65 M66 2019 |
| ISBN | bn:9782742798247 |
| ISSN | in:0018-165x |
| Keyword | kw:childhood
kw=early childhood |
| Language | ln:fra |
| Editor | pb:Springer
pb=Cambridge University Press |
| Subject | su:chemistry
su=chemistry, organic |
| Title | ti:Trainspotting
ti=Brave New World |
| Year of Publication | yr:2020
yr:2010-2019 |
| Barcode | bq:X38579059 |
| Format | x0:artchap
Format abbreviations |
Do not use spaces between index abbreviations and punctuation marks ( : or =), or between punctuation marks and keywords. Ex. : au=shakespeare william
Clicking on index words
Clicking on author (au=), subject (su:) or collection (se:) in items in results lists automatically launches a new index search.
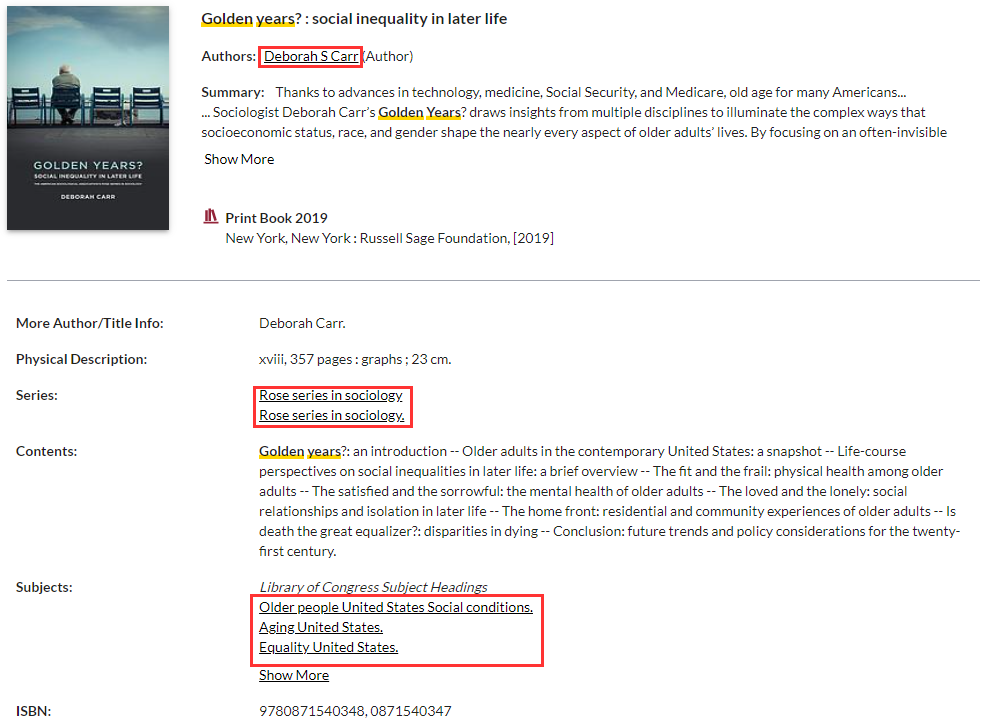
Examples of new searches generated by clicking on item links:
- au=Carr, Deborah S
(Displays all of the author's publications) - se:Rose series in sociology
(Displays all of the publications in the series) - su:Aging United States
(Displays all publications related to the subject matter)

Facets and sorting to refine a search
Facets
Facets are characteristics unique to a group of items and make it possible to refine the search results obtained based on one or more characteristics. Facets appear to the left of the search results in Sofia.
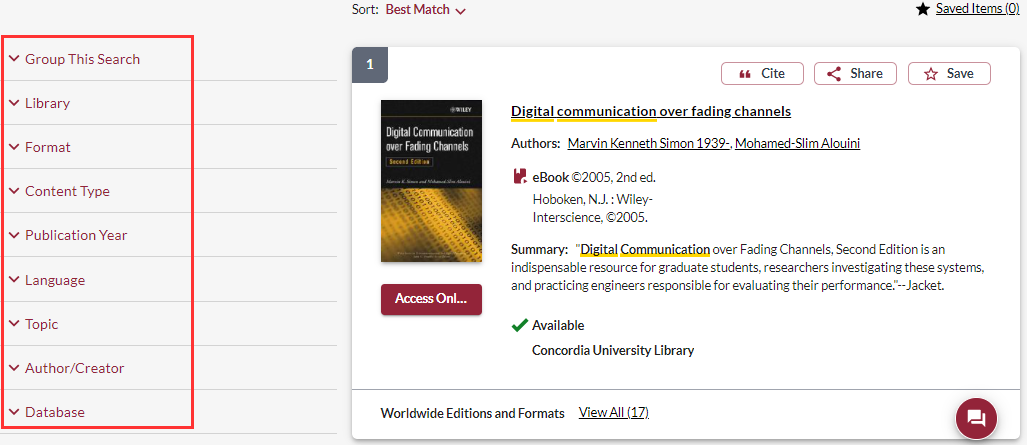
- Group This Search (Group Related Editions): allows all the editions of a work (1st, 2nd, 3rd editions) to be grouped together under a single record when they are held by the same library. If the option is unchecked, each of the editions will be displayed as an independent document. This option is useful when the most recent edition is already checked out or to hide duplicates of the same title.
- Refine This Search (Expand Search with Related Terms): allows you to improve the keywords used with standardized terms from recognized thesauri (AAT, LCSH, MeSH, RVM, etc.) or with automatically translated search terms. This facet is useful for quickly finding relevant documents in a language other than the one used to search. When activated, the detail of the expansion appears in the form of an information bar placed at the top of the screen, allowing the user to know the terms that have been used to refine their initial search.
- Library: allows you to modify the scope of the search according to three levels of collections: home institution, academic libraries in Quebec or libraries worldwide. You can limit the results to the documents available at a specific library within your institution, extend the search to all Academic Libraries in Quebec, or explore the collections of libraries around the world. This facet is useful for locating titles of documents that have never been acquired by your institution, with a view to requesting them through the interlibrary loan service.
- Format: limits the search according to a specific type of document (article, book, video, periodical / magazine, etc.) as well as the specific formats relating to it (print, digital, VHS, etc.). This facet is useful for planning the use of specific devices. It is possible to select several options within this facet.
- Content Type: limits the search to certain categories of content (biographies, novels, open access publications, etc.). This facet is useful for easily locating literary subgenres or open access content.
- Publication Year: limits the search to a specific year (eg: 2017), to a time interval (eg: last 5 years) or to a specific interval of publication years (eg: from 2011 to 2017). This facet is useful for locating an author's publications in a specific year, for limiting the search to recent publications, or for locating documents published during a specific time interval.
- Language: limits the search according to the language in which a document was published. This facet is useful for locating items in the user’s language of choice.
- Topic: limits the search to a specific field of study, or a more precise sub-category. The topics in this facet come from the OCLC Conspectus, a hierarchy of topics organized by classification number (Dewey, LC or NLM) or by division / category. Topics are displayed according to the number of results identified (from the most numerous to the least numerous). This facet is useful for distinguishing between different contexts for the same search term.
- Author/Creator: limits the search to a specific author or creator. Listed in alphabetical order, the top 25 most commonly found names in the search results are displayed. This facet is useful for distinguishing works with a similar title or for locating documents written by recognized organizations. When the search finds a large number of results, similar names of authors / creators are grouped together.
- Database: limits the search to specific sources of data.
Sorting Options
Search results may be sorted by relevance or bibliographic field.
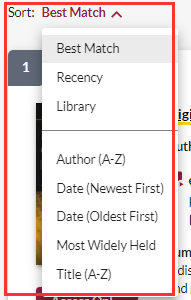
Sorting by relevance: this type of sorting takes into account the number of occurrences of a search keyword in the item records. Three options for sorting by relevance are available:
- Best match: this sorting option prioritizes items with the highest number of occurrences of a keyword in a record first, while emphasizing the title of the document.
- Recency: this sorting option prioritizes items with the highest number of occurrences of a keyword in a record first, while also emphasizing the publication date of a document. Not to be confused with the Date (most recent) option, for which the number of occurrences of a keyword does not take precedence over the order in which the results are displayed.
- Library: this sorting prioritizes items with the highest number of occurrences of a keyword in a record first, while emphasizing the collections available at the home institution.
Sorting by bibliographic field: this type of sorting takes into consideration the bibliographic information entered in a specific field for each item. Several sorting options by field are available:
- Author (A to Z): search results are sorted alphabetically, according to the last name and first name of the first author mentioned in the item record.
- Date (Newest First): search results are sorted in chronological order (from most recent to oldest) according to the publication date in the item record. Not to be confused with Recency (relevance), for which the publication date is a secondary criterion in the order in which the results are displayed, the primary criterion being the number of times a keyword is found in a record.
- Date (Oldest First): search results are sorted in chronological order (oldest to the most recent) according to the publication date in the item record.
- Most widely held: search results are sorted according to the number of libraries around the world holding a copy of the item found by the search (from most held to least held). This option is useful for knowing the essential titles related to the keywords used during the search.


